The most versatile tool for monitoring and analyzing filamentary structures for neuroscience, cell biology and vascular research. This is the new IMARIS 10.0!
The latest version of the Imaris 10.0 analysis software features intuitive workflows and comprehensive analysis tools, while providing high performance rendering, processing and ultimately beautiful images.
The new Filament Tracer 10.0 combines the versatility of an Autopath intensity-based method with a unique machine learning approach to provide the most flexible tool on the market for tracing many types of neurons, blood vessels, and fiber cell components.
Key features and benefits of the new Imaris 10:
- Block computation of detected structures - tracking images larger than 2 GB and significantly faster computation and visualization of detected objects
- Faster rendering of filamentary objects - seamless interaction (rotation, selection, etc.) of filamentary objects and their subcomponents
- Multi-scale seed points - accurate detection of vessels and neurons of different diameters
- Pointclassification using machine learning - improving the quality of results for images of average quality
Try a free 10-day trial!
The link to download the trial version can be found on the manufacturer's website HERE
Imaris 10.0 Release Note to read HERE
Application:
- Neuroscience
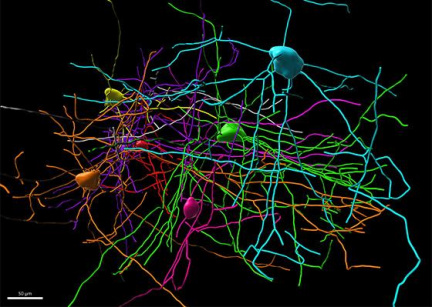 The Filament Tracer module in Imaris 10.0 allows 3D reconstruction of neurons and analysis of arborization (branching of neuronal processes). It can distinguish different structures such as axons and dendrites, soma, dendritic spines, microglia or astrocytes. Imaris 10.0 extends the proven autopath method for tree-like structures with machine learning classification and a multi-scale seed point method for more accurate and repeatable detection (using Imaris Batch). A wide range of neuron-specific measurements such as dendrite length, orientation, diameter, branching level, dendritic spine density, and spine shape analysis and classification are computed.
The Filament Tracer module in Imaris 10.0 allows 3D reconstruction of neurons and analysis of arborization (branching of neuronal processes). It can distinguish different structures such as axons and dendrites, soma, dendritic spines, microglia or astrocytes. Imaris 10.0 extends the proven autopath method for tree-like structures with machine learning classification and a multi-scale seed point method for more accurate and repeatable detection (using Imaris Batch). A wide range of neuron-specific measurements such as dendrite length, orientation, diameter, branching level, dendritic spine density, and spine shape analysis and classification are computed.
- Cell biology
 The increasing availability of super-resolution light microscopy allows researchers to observe the components of cells in greater detail. Thanks to a new algorithm in the Imaris 10.0 Filament Tracer module, some intracellular structures such as microtubules, endoplasmic reticulum or actin filaments can be easily detected as filamentous structures. The combination of the autopath-intensity algorithm with machine learning classifiers enables fast and accurate detection of these structures and unlocks several measurements unavailable for other Imaris models, such as segment length or total length of the intracellular structure, straightness, mean diameter or orientation measurements.
The increasing availability of super-resolution light microscopy allows researchers to observe the components of cells in greater detail. Thanks to a new algorithm in the Imaris 10.0 Filament Tracer module, some intracellular structures such as microtubules, endoplasmic reticulum or actin filaments can be easily detected as filamentous structures. The combination of the autopath-intensity algorithm with machine learning classifiers enables fast and accurate detection of these structures and unlocks several measurements unavailable for other Imaris models, such as segment length or total length of the intracellular structure, straightness, mean diameter or orientation measurements.
- Vascular research
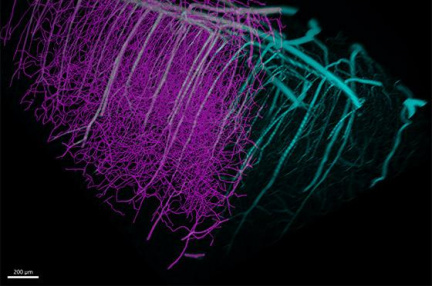 Scientists interested in blood vessel tracking gain a new Loop algorithm with Imaris 10.0 to efficiently detect dense vascular networks in the brain or other organs. A characteristic feature of a vascular network is the large difference in diameter between major dense blood vessels and small capillaries. For this reason, a new multi-scale seed point function has been introduced in Imaris 10.0 Filament Tracer for accurate detection and measurement. From the blood vessel model, researchers can derive measurements such as segment length, total blood vessel length, diameter, mean segment intensity, and segment orientation.
Scientists interested in blood vessel tracking gain a new Loop algorithm with Imaris 10.0 to efficiently detect dense vascular networks in the brain or other organs. A characteristic feature of a vascular network is the large difference in diameter between major dense blood vessels and small capillaries. For this reason, a new multi-scale seed point function has been introduced in Imaris 10.0 Filament Tracer for accurate detection and measurement. From the blood vessel model, researchers can derive measurements such as segment length, total blood vessel length, diameter, mean segment intensity, and segment orientation.