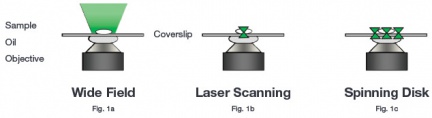
In contrast to widefield imaging with the classical fluorescence microscopy method, the signal from the sample that comes from outside the focal plane is suppressed in confocal microscopy. This allows the observation of slides of greater thickness while maintaining contrast and a high signal-to-noise ratio. On a confocal microscope equipped with a detector or camera and a workstation with the appropriate software (Imaris), the user is then able to digitally reconstruct a three-dimensional model of the entire slide (3D visualisation). There are two main approaches:
- CLSM(Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy)
- SDCM (Spinning Disc Confocal Microscopy)
The disadvantage of laser scanning confocal microscopy is the concentration of a very intense laser beam on each imaged point (pixel). This exposes the slide to the toxic effects of light for a long time. In addition, it is necessary that the light from the laser beam hits all the imaged points sequentially, which results in a significant limitation of the scanning speed, especially at high resolution (e.g. 2048 x 2048 pixels). The suppression of the signal from outside the focal plane is achieved by the use of a variable sized 'pinhole' which is placed in front of the detector.
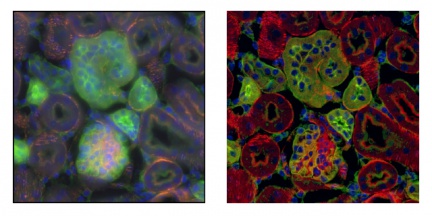
Figure 2: Widefield (left),confocal microscopy (right). One optical plane (60× 1.2 NA). Images taken in widefield mode contain signal from outside the focal plane. The rotating disk-based confocal microscope provides sharp images from a single focal plane with more detail as well as higher contrast and dynamic range. Dragonfly, Andor (Andor, 2016).
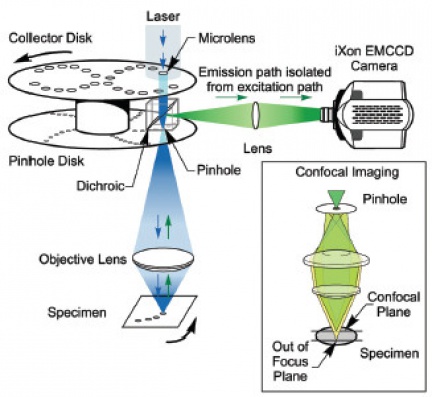
Confocal microscopy based on a spinning Petran/Nipkow disk (spinning disk) achieves very fast, high-resolution image acquisition. The excitation optical path passes through a so-called spinning disk containing a high number of "pinholes" that ensure the confocality of the acquired image (Figure 3). Just by rotating the disk by a few degrees we achieve coverage of the entire field of view (speeds around 6000 rpm - Dragonfly). Another advantage of rotating disk-based confocal microscopy is the use of sensitive and very fast cameras with high dynamic range for image detection (Zyla/iXon).
Key advantages of spinning disk
- High scanning speed (hundreds to thousands of frames per second)
- High sensitivity (quantum efficiency of cameras up to 95%)
- Low photo-toxicity
- Reduced photo-bleaching
Report source: "Spinning Disk Confocal - A Technical Overview..." Accessed November 25, 2016 www.andor.com/learning-academy/spinning-disk-confocal-a-technical-overview